Etching Process
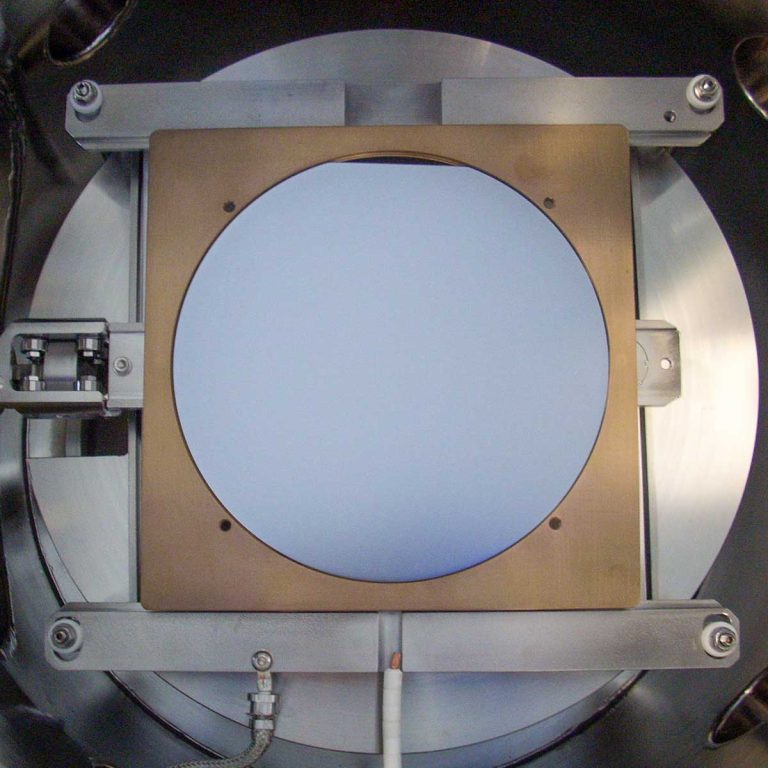
Inductive Coupled Plasma RIE
ICPRIE
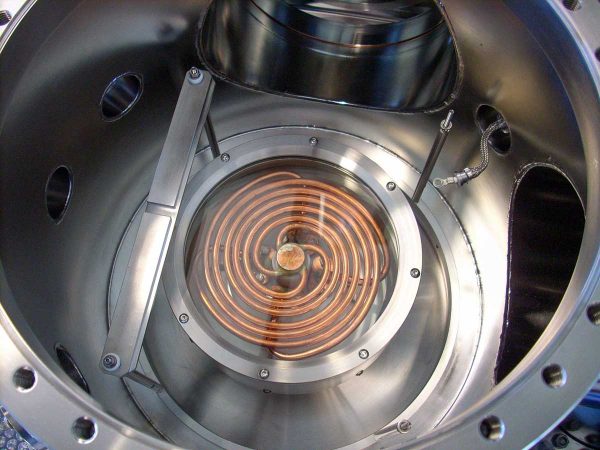
Inductive Coupled Plasma Reactive Ion Etching (ICPRIE) is a plasma-based etching method used to remove material from a substrate surface. ICPRIE is especially useful for deep reactive ion etching (DRIE) of silicon, which is critical in advanced MEMS applications for creating high aspect ratio microstructures. During ICPRIE, gas species are activated within the plasma discharge area of the inductively coupled plasma (ICP) source and transported to the substrate surface through diffusion. A negative electric bias applied to the substrate then accelerates these species to the material surface to perform etching. A mask is can be used to pattern the substrate surface, allowing for selective etching in certain areas. It is equipped with an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) source alongside a plasma a source applied directly on the substrate, enabling better etching selectivity and higher aspect ratios of the structures produced
Applications
ICP-RIE has a wide range of applications, from structuring sensors (GMR, TMR) in MEMS production to realizing trenches and vias in low and high power semiconductors. The Bosch Process is used to fabricate trenches, holes, and pillars for various device applications, and the materials that can be etched are the same as in conventional RIE
- Consumer Electronics
- Solar energy
- Aerospace and Defence
- Biomedical and Healthcare
- Optics and Photonics
Key features
- Substrate cooling
- Single or multiple automatic or manual load lock and manipulators
- Optional optical emission spectrometer for insitu plasma diagnostics and End Point Detection
- Optional real-time, in-situ, plasma etch depth monitoring and end point detection plus colinear wafer vision system
- HV or UHV configuration
- Different reactive gases (02 , H2, N2, C2H4 , CF4, SF6, etc.) can be used during etching process
Etched materials
Metals, Oxides, Nitrides, Carbides, Semiconductors, Carbon Based Materials, Organics
Similar technologies
Inductive Coupled Plasma Reactive Ion Etching (ICPRIE)
the best choice for high speed etching



