CVD Process
Metalorganic CVD
MOCVD
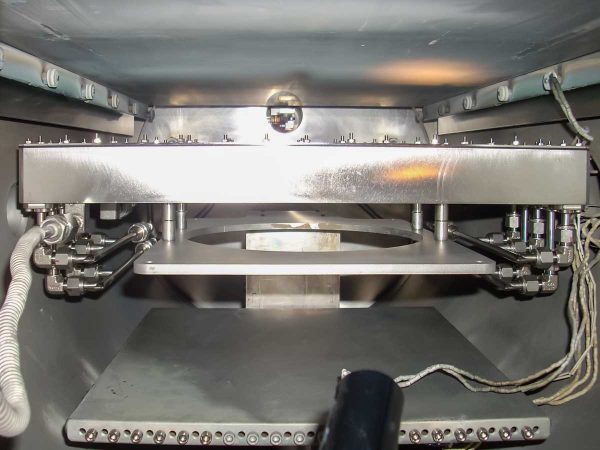
Metalorganic Chemical Vapor Deposition is a method of depositing thin films on a substrate surface through
a chemical reaction between one or more reactive gases and the substrate.
Using this method is it possible to create high purity dielectric, metallic or semiconducting thin films. In the
MOCVD process, ultrapure metalorganic precursor gases are introduced into a reactor, where they undergo
pyrolysis on the semiconductor wafer. As a result, the subspecies are absorbed onto the wafer surface.
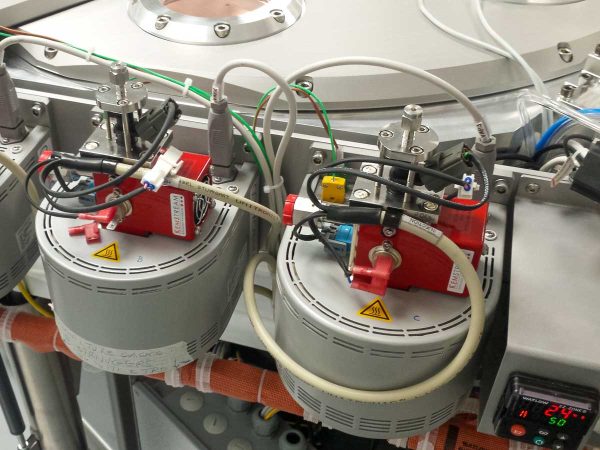
The metalorganic precursor is introduced into the process chamber via a system known as “bubbler”, which
uses an inert carrier gas (such as He or Ar) to transport the precursor liquid into the chamber. MOCVD
operates at moderate pressures (1 to 760 Torr) in the gas phase.

Applications
MOCVD is commonly used in the production of laser diodes, LEDs, and semiconductors for
advanced optoelectronics, high power and highspeed electronics, enabling mass production of semiconductor heterostructures via bandgap engineering. Furthermore, MOCVD can be utilized to precisely fabricate 0D, 1D, and 2D nanomaterials.
- Consumer Electronics
- Solar energy
- Aerospace and Defence
- Healthcare and medical devices
- Optics and Photonics
- Power Electronics
- Research
Key features
- Metalorganic liquid precursors
- HV or UHV configuration
- Reactive gases (SiH4 , NH3 , H2 , CH4 , N2 , etc.) and/ or liquid precursors controlled directly from the software
- Optional vapor source controller for liquid Precursor with tank/cylinder in a closed cabinet for safe refill
- Optional single or multiple automatic or manual load lock with optional pre-heating and/or plasma treatments
- Optional wide range optical thickness monitor for the control of layer thickness
Deposited materials
Oxides, Nitrides, Carbides, Semiconductors, Carbon Based Materials, Organics
Similar technologies
Metalorganic CVD
the best choice for obtaining compound materials with finely tailored composition starting from liquid precursors



